Methods of keratoconus treatment
1. Glasses and contact lenses
Using glasses or soft contact lenses in the early stages of keratoconus, which involves myopia or regular astigmatism aids the patient, however, with the progress of the disease and the emergence of irregular astigmatism, these methods do not provide the patient with proper vision any longer. Prescription of glasses by the ophthalmologist highly enhances vision. However, the disease has a progressive nature; thus, the prescribed number will be changed.
2. Hard lenses
With the progress of keratoconus, the glasses will be of no use in correcting the vision, and hard contact lenses should be used since they are more capable of correcting irregular astigmatism. These lenses on the cornea cause the irregular surface of the patient’s cornea to be covered by a flat surface and the light refraction properly occurs. Patients can use hybrid lenses (a combination of hard and soft) if they cannot stand hard lenses.
3. Cross Linking or CXL
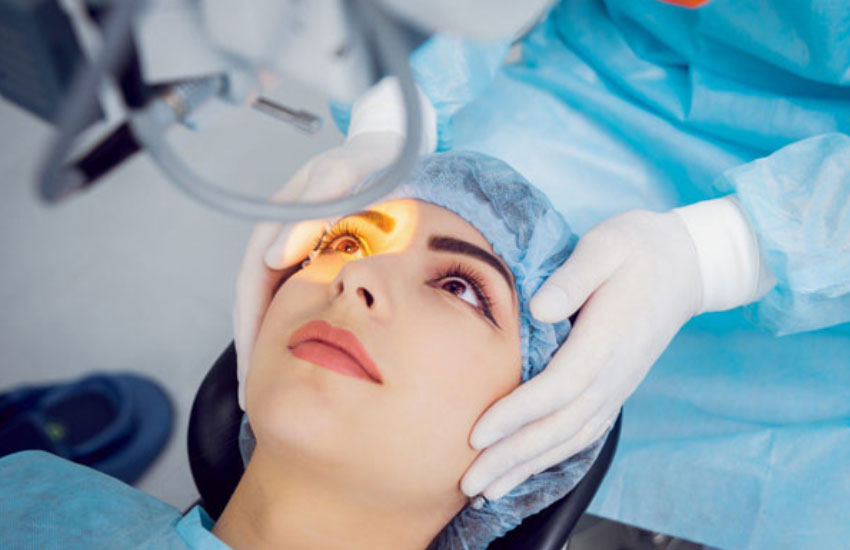
A new treatment for keratoconus, raised in recent years, is the cross-link between corneal collagen strands using ultraviolet radiation and riboflavin, which brought about a new development in preventing the keratoconus progress and new promises. In this method, after removing the surface cornea cells (epithelium), for 30 minutes (once every 3 minutes) drops of riboflavin 0.1% is poured into the eye, and then, over the next thirty minutes, once every 5 minutes, riboflavin is dropped in the eye, then the ultraviolet is radiated to the cornea, which increases the cross-links between corneal collagen strands and, thus, enhances the corneal strength.
The best volunteers of this method include:
-
Patients with recent diagnosis of keratoconus
-
Young and middle-aged people with progressive disease
-
Those whose contact lens does not fit well
-
The cornea thickness should be at least 400 microns
-
The patient should not be pregnant or breastfeeding
4. Use of intacs cornea rings and myoring
There is a great development in treating the disease when the patient is unable to stand contact lenses. Using these rings not only improves vision with and without glasses, but also leads to better lens tolerance and prevents the progress of keratoconus. A study on this method has been underway in recent years and the results indicate a relative improvement in patients, though it has not been shown that this method prevents the keratoconus progress. These rings contribute to the improvement of visual acuity by decreasing the amount of irregular astigmatism, however, it should be noted that the success rate of intracorneal rings is quite variable and varies from person to person, and in the event of a treatment failure, the patient eventually needs corneal transplantation.
5. Corneal transplantation
With further keratoconus progress, using contact lenses and intracorneal ring parts will not increase the vision and it becomes impossible to use contact lenses due to corneal opacity, resulting in intolerance to the contact lens. Corneal transplantation should be used at this stage. Corneal transplantation is a standard treatment for patients with advanced keratoconus which often yields good results. This operation is along with approximately 95% success, however about 10%-20% of keratoconus patients need transplant surgery. After corneal surgery, 60% of patients require contact lenses to correct vision, and recurrence of keratoconus rarely happens after transplantation.